What is data science?
Data science is more than just statistics. It’s an interdisciplinary approach to turning raw data into actionable knowledge – through a mix of mathematical methods, coding, and subject matter expertise. The goal: identifying patterns, predicting developments, and automating decision-making processes – in short, using data to drive better solutions.
Data-driven solutions in noise control and civil engineering
In noise control, data-driven models help to better plan noise mitigation measures. Time series analyses allow us to study long-term noise level trends – helping to pinpoint critical time windows. Machine learning models also make noise predictions more realistic.
A concrete example: Quietpave-check.ch – a G+P-developed tool for AI-based analysis to select the most suitable low-noise road surfaces. It forecasts acoustic performance based on local factors like traffic volume, surroundings, elevation, and climate – including a cost-benefit assessment.
In civil engineering, sensors and image sources allow continuous monitoring of conditions – and data science helps to analyze them:
-
Automatic traffic classification from video footage: vehicle types, frequencies, patterns – in real time, with high accuracy.
-
Trains can also be classified automatically: including train type, length, and speed – all from video only.
-
Image recognition for rock type classification – more efficient and objective than manual methods.
-
Even road surfaces can now be automatically typed based on photos – a valuable foundation for planning, condition assessment, and maintenance.
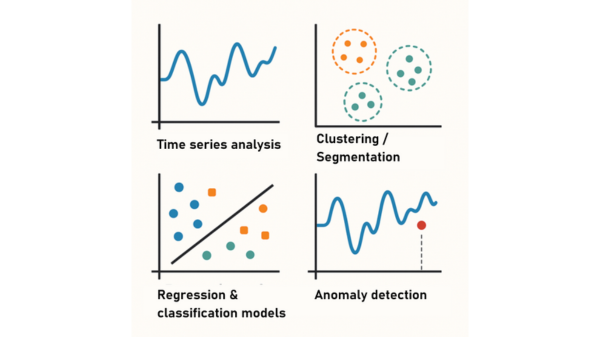
Our toolbox: Proven methods for data-driven projects
We draw from a broad set of well-established methods:
-
Time series analysis: to identify trends, patterns, and seasonality in measurement data.
-
Clustering & segmentation: grouping similar data points for pattern recognition or typology.
-
Regression and classification models: predicting numerical values or categories such as noise levels, pavement condition, or rock type.
-
Anomaly detection: automatically identifying outliers or unusual system behavior.
Our strength lies in combining these methods with deep expertise in noise control and civil engineering – and in our ability to meaningfully connect and interpret even complex data sets.
Don’t just collect data – use it: We support you
You have data – but no clear strategy yet? Together, we identify potential, analyze existing sources, and show you how to integrate data-driven processes into your workflows. From data preparation to model development to real-world implementation – we help you turn data into informed decisions.
/www.gundp.ch/file/2834/ChatGPT%20Image%2024.%20Juni%202025%2C%2008_51_52.png)
/www.gundp.ch/file/1625/CPX_Jaun_Quadratisch.jpg)
/www.gundp.ch/file/2370/Titelbild_LAB_LCA_v4.png)
/www.gundp.ch/file/2741/Blog_acoustic-assessment-of-pv-systems-on-motorways.png)